A Technical Walkthrough of Hash Time Locked Contracts and Lightning Channel Operations
This post will walk through the different operations of a Lightning channel by following a long-running example with plenty of explanatory diagrams. First, we explore how Hash Time Locked Contracts (HTLCs) are added to a channel and how channel peers commit to a new state including these HTLCs. Next, we discuss how a channel’s normal flow is re-established after a disconnection. And finally, we finish with how a cooperative channel closure happens. These topics are all covered in Bolt 2 for those interested in learning more. Note that some of these operations will change with Taproot channels, which will be detailed in a future post.
Preliminaries
Here are a few links that cover some preliminaries that might be useful for understanding this blog post:
- Why channel peers have an asymmetric state and how they go about updating this state in a trust-less way: Updating State.
- What HTLC outputs look like on a commitment transaction: HTLC deep-dive.
- How two nodes go about opening a channel: Opening and announcing a pre-taproot LN channel.
Normal Channel Operation
Setting the scene
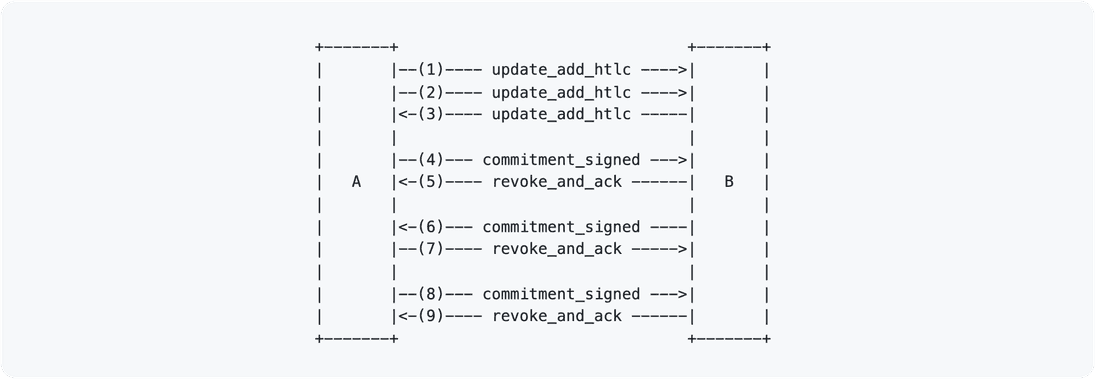
Alice and Bob (hello old friends!) have successfully opened their channel. They
have both seen that the funding transaction has confirmed, and they have
exchanged the channel_ready message with each other to indicate that they are
ready to use the channel. The state of their asymmetric commitment transactions
currently look as follows:
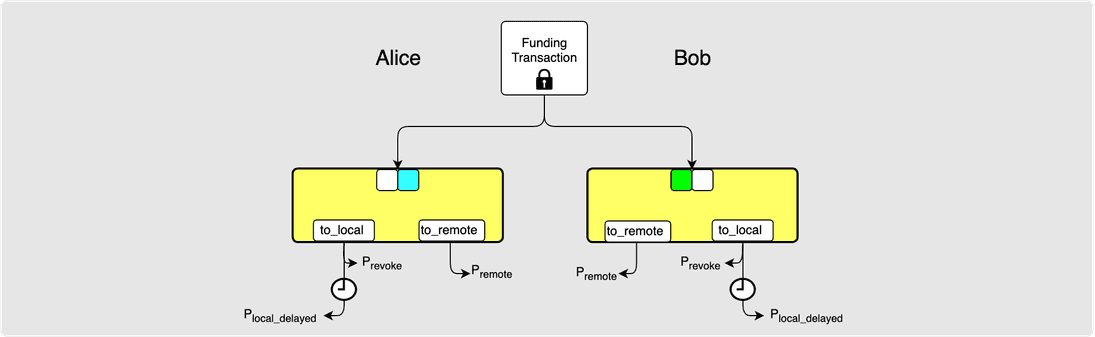
Both commitment transactions spend the 2-of-2 multi-sig funding transaction
output. Spending from this output requires a signature from both parties. The
signatures are represented by the two boxes at the top of the commitment
transactions. You can see from the diagram that Alice’s commitment transaction
has a signature from Bob represented by the blue box (say it with me: “Bob is
blue!”) and Bob has a signature from Alice for his commitment transaction
represented by the green box (“Alice is green” doesn’t have quite the same ring
to it). Each commitment transaction also has the to_local and to_remote
outputs which pay the respective parties their current channel balance. Both
Alice and Bob have the ability to sign their own commitment transaction at any
time and broadcast it to the Bitcoin network. This would be a force close.
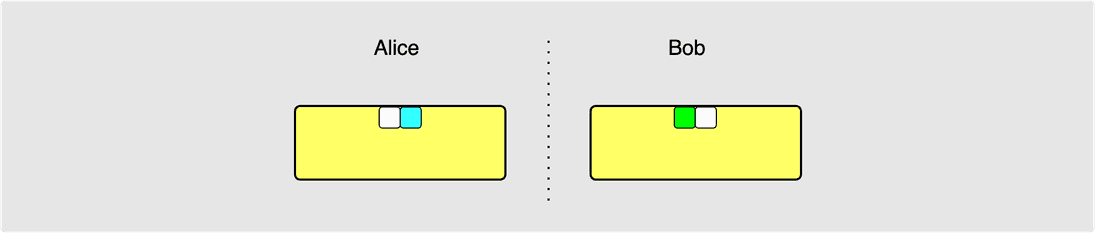
For the sake of making the next few diagrams in this article a bit simpler, I
am going to ignore the funding transaction along with the to_local and
to_remote outputs for a while since our initial focus is going to be on adding
and removing HTLC outputs. So the above diagram can instead be represented as
follows:
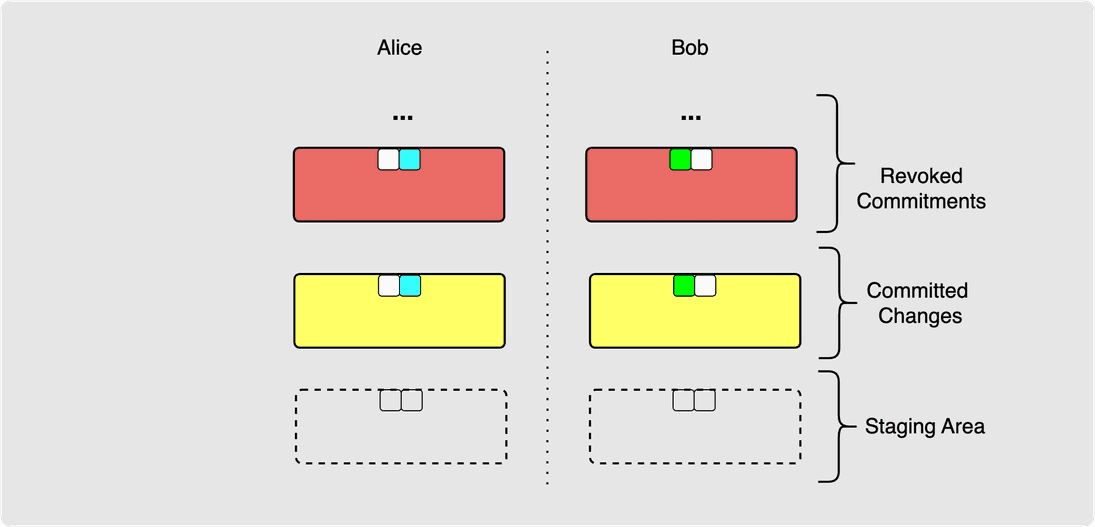
A red coloured commitment transaction, as shown below, represents past, revoked commitment transactions. If Alice or Bob were to sign and broadcast one of their older revoked commitment transactions then the other side would be able to sweep all their funds. So these revoked transactions can effectively be considered invalid. The yellow commitment transactions represent the latest, valid set of commitment transactions. These are the commitment transactions that would be broadcast in a force close. Then finally, each side has what can be thought of as a “staging area” where changes to the commitment transaction can be proposed. Later on, either side can decide when it wants its counterparty to commit to the changes in their staging commitment transaction. For those of you who love a good analogy - this is very much like a git workflow: past commits are out of date, but they tell a nice story of what has happened, your latest committed changes represent the current state of your project and any changes that are not yet committed are in staging.
Adding an HTLC
When either Alice or Bob want to send a payment across the channel in question
(which would happen if either of them wanted to send a payment themselves or if
they are routing another node’s payment) then they would need to propose the
inclusion of the HTLC to their channel peer. This is done with the
update_add_htlc message:

The channel_id is used to communicate which channel this change should take
place on, the id is an always-incrementing identifier for this proposed
change from the sender. The amount_msat is the amount that should be attached
to the HTLC output, the cltv_expiry is the block height that the HTLC should
expire at and finally the onion_routing_packet and optional blinding_point
both contain data that the recipient will use to determine where next to send
the payment.
Something that definitely took me a while to wrap my head around is the fact
that the sender of this message does not put this update in their own staging
area commitment transaction yet. This is because the update is still "pending
on the receiver" because the sender has not yet received any acknowledgement
from receiver for the new update. This is to allow for the case where one peer
sends an update and then immediately receives a commitment_signed message
(more details on this later). In that case, there should be no ambiguity around
which updates are included in the transaction being signed. Hopefully this makes
more sense as we work through the example.
⚙️ Step 1: Alice -> Bob: update_add_htlc(A1)
Ok so let’s say that Alice sends Bob an update_add_htlc. Let’s call this
HTLC A1 since it is the first one that Alice (A) is sending to Bob. If Bob
is happy with all the fields in the message, then he adds the HTLC to his
staging area commitment transaction and Alice marks the HTLC as pending on
Bob's side but does not yet add it to her staging commitment transaction:
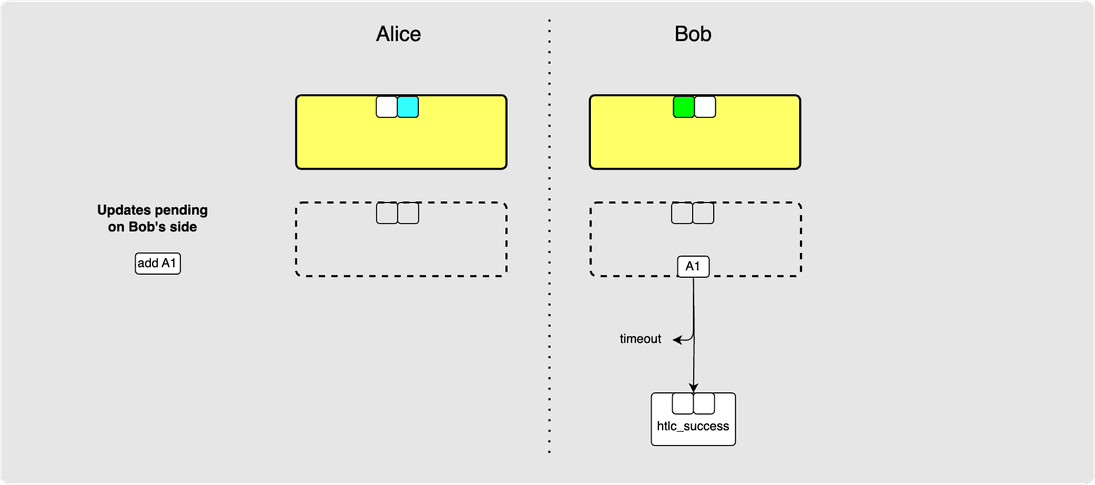
Note that neither side has actually committed to this HTLC and so if Bob is a
routing node for this payment, he should not yet send update_add_HTLC to the
next hop in the route until A1 has been irrevocably committed. An HTLC
addition or removal is only considered irrevocably committed once both
parties in the channel have committed to the commitment transaction with or
without it respectively.
Something that the more simplified diagram fails to show is that Alice's main
output in Bob's staging commitment transaction (ie, the to_remote output)
will now have the value of the added HTLC subtracted (along with the fees to
cover the extra output). If the HTLC ends up succeeding then this amount will be
added to Bob's output and if it ends up failing, then it will be re-added to
Alice's output.
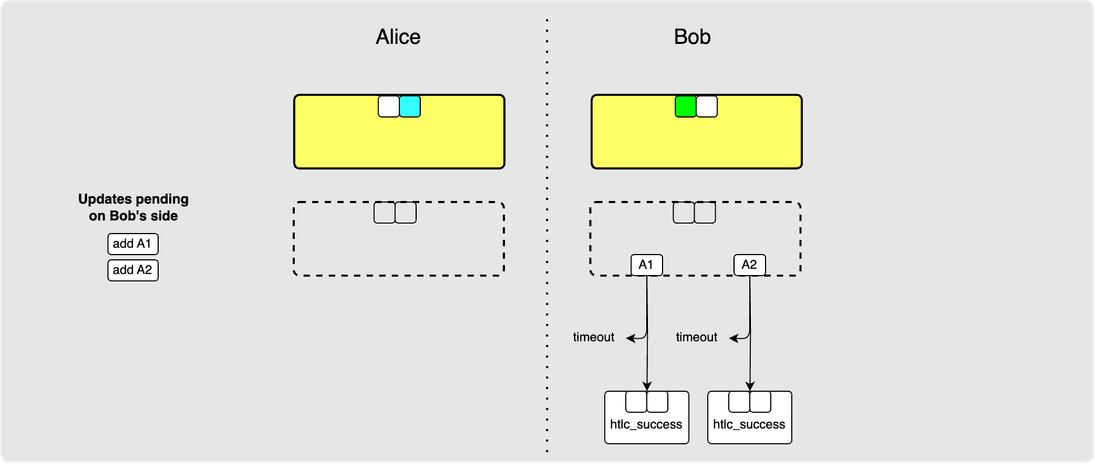
⚙️ Step 2: Alice -> Bob: update_add_htlc(A2)
Even if they have not committed to HTLC A1 yet, that does not stop them from
adding more changes to the staging area. So Alice is more than welcome to
propose a new HTLC, A2, to Bob:
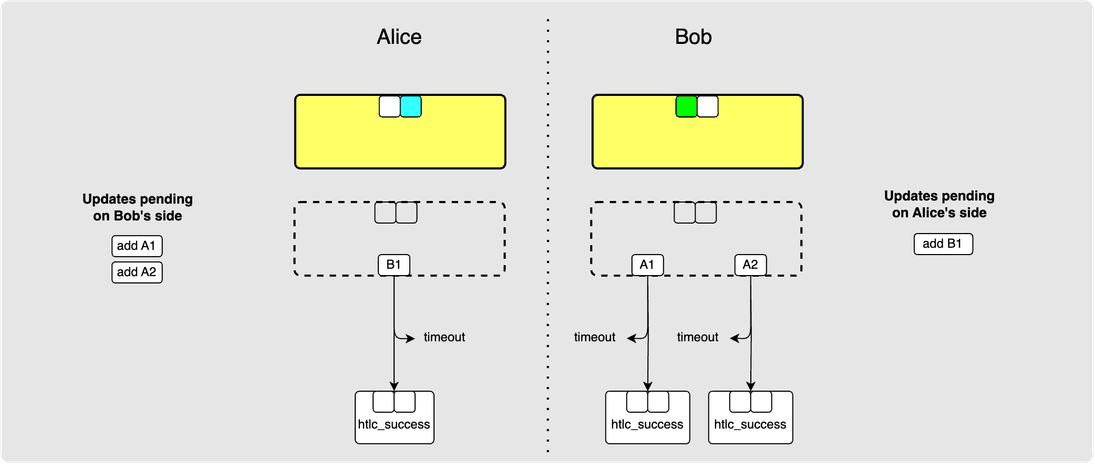
⚙️ Step 3: Bob -> Alice update_add_htlc(B1)
Similarly, Bob can suggest a change B1 to Alice:
Committing to the current state
At some point, one of the peers will want to make sure that the other peer has
committed to the latest set of changes and revoke the previous valid state. This
is done by sending the commitment_signed message:
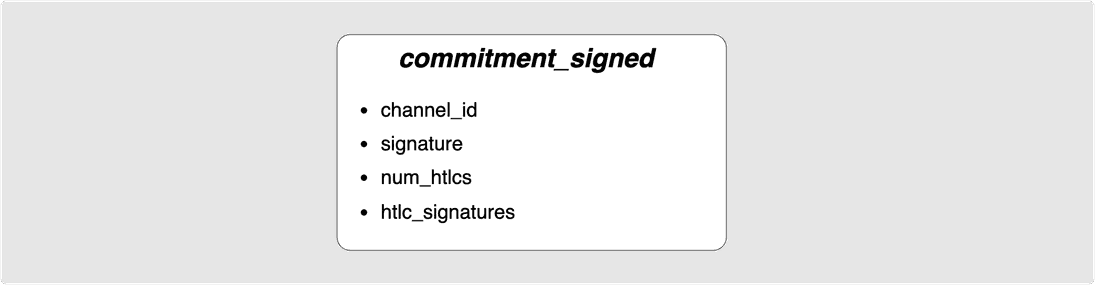
The channel_id once again refers to the channel in question. The signature
is the sender's signature for the remote party’s staging area commitment
transaction. num_htlcs refers to the number of HTLCs that the sender expects
to be on the remote commitment transaction and this is then followed by
htlc_signatures which is an array of num_hltcs signatures which are the
sender’s signatures for each of the second-level HTLC transactions that the
remote party would need to broadcast if they were ever to force close the
channel. If you need a reminder about why the second-level HTLC transactions are
needed, give this post a read.
⚙️ Step 4: Alice -> Bob: commitment_signed
Let’s say that Alice sends this message to Bob. Bob will now have all the required signatures from Alice to broadcast his staging-area commitment transaction:
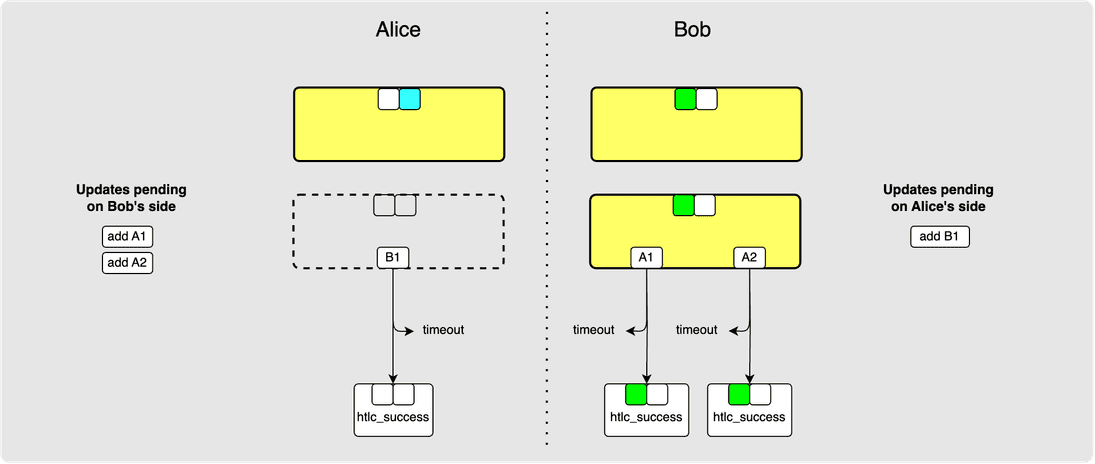
Notice that Alice knew that her signature would need to cover the A1 and A2
HTLCs. This is fine because the underlying transport is guaranteed to
be reliable and ordered meaning that if Bob was to receive Alice's
commitment_signed message then it means that he definitely received her
update_add_htlc messages for A1 and A2. Alice and Bob both know that the
signature should not cover the B1 HTLC since Alice has not sent an
acknowledgement for it yet.
Another thing to notice is that Bob now actually has two valid commitment transactions since he has not yet revoked his previous state. He is, however, incentivised at this point to revoke his previous commitment transaction since the HTLCs on the new state are either:
- Payments to Bob himself meaning that he gains from committing to the new state. If he doesn’t commit to the new state, then Alice won't either and so there would still exist a version of a commitment transaction that does not pay Bob his incoming funds.
- Similarly to the above point, if Bob is routing a payment, then he is also incentivised to try to get the HTLC irrevocably committed since he would earn routing fees if the payment succeeds.
- Finally, if Bob is making the payment himself, then the first state would in fact be more desirable to him since he strictly has less funds in the second state. However, the merchant that Bob is making the payment to won't release the goods being purchased unless funds come through which won't happen if Alice does not pass on the HTLC which she won't do unless it has been irrevocably committed to. So again, Bob is incentivised to revoke his previous state.
⚙️ Step 5: Bob -> Alice: revoke_and_ack
In response to Alice’s commitment_signed, Bob sends the revoke_and_ack
message:
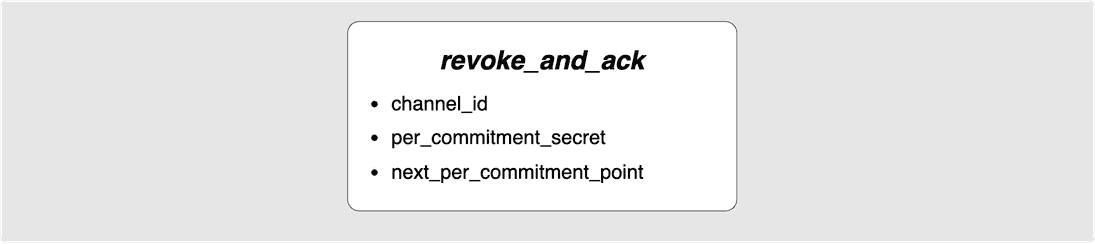
The per_commitment_secret provides Alice with the information she needs in
order to be able to spend any revocation path on Bob’s previously valid state.
See this post for more details about how revocation works.
The next_per_commitment_point gives Alice the information she needs in order
to derive the revocation public key that will be used in Bob’s next commitment
transaction. Once Alice receives this message, Bob’s previous commitment
transaction has successfully been revoked. Note that this message explicitly
acknowledges the commitment_signed message sent by Alice and by extension,
since messages delivery is reliable and ordered, it also implicitly acknowledges
the update_add_htlc messages that Alice sent for A1 and A2. Alice can
therefore finally add A1 and A2 to her staging area commitment transaction
since they are no longer pending on Bob's side:
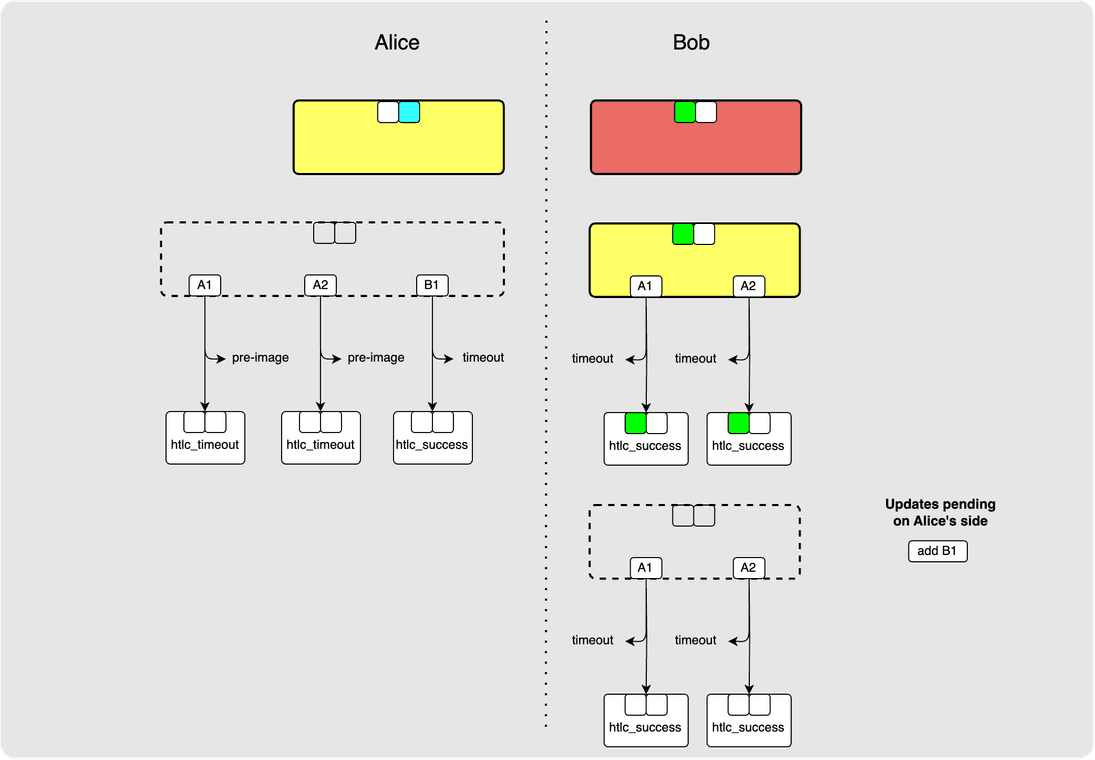
Let’s clean up the diagram a bit…
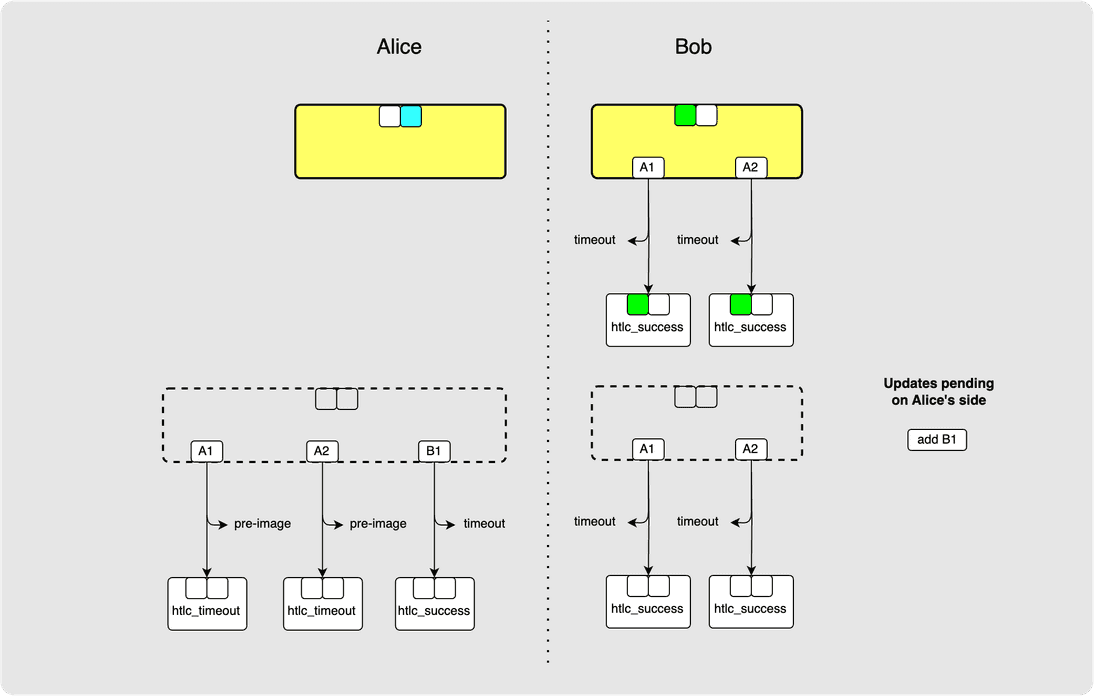
That’s better.
From the above diagram, notice that Alice's and Bob’s latest commitment transactions are actually out of sync. This is fine since none of the updates have been irrevocably committed yet. That might seem hard to believe since the commitment transactions look so different so let’s walk through the consequences of either of these transactions ending up on-chain from the perspective of both sides.
-
From Alice’s perspective:
- if her commitment transaction is broadcast, she gets back her original
to_localamount. - if Bob’s commitment transaction is broadcast, then Alice's offered HTLCs
(such as
A1andA2) will be on-chain. For offered HTLCs, Alice is sending sats out meaning that herto_localwould be lower. But, if Bob was a router node for these HTLCs then he would not have forwarded them as they are not yet irrevocably committed meaning that he won't receive the pre-images required to claim these HTLCs and Alice would be able to get her funds back via the timeout path. If Bob was the recipient of these HTLCs, then he would be able to produce the pre-image to claim the HTLCs, but then Alice would see the pre-image on-chain and would be able to claim the incoming HTLCs from their incoming channel and would thus have earned routing fees.
- if her commitment transaction is broadcast, she gets back her original
-
From Bob’s perspective (very similar to the logic for Alice):
- if Alice’s commitment transaction is broadcast, Bob gets back his funds via
the
to_remoteoutput. - If Bob had to force close via his commitment transaction, then HTLCs offered
to him (like
A1andA2) would be on-chain, if Bob was routing these, then he would not have forwarded them on since they are not yet irrevocably committed. He thus won't be able to claim the success path but that is fine since the funds for these did not come out of his balance. If Bob was the final destination for these, then he would be able to claim them via the success path.
- if Alice’s commitment transaction is broadcast, Bob gets back his funds via
the
⚙️ Step 6: Alice -> Bob: update_add_htlc(A3)
I want to really nail down the point that the commitment transactions can remain
out of sync indefinitely and that Bob does not need to send commitment_signed
just because Alice did. So, for the sake of the example, let’s say that Alice at
this point sends yet another HTLC, A3, to Bob:
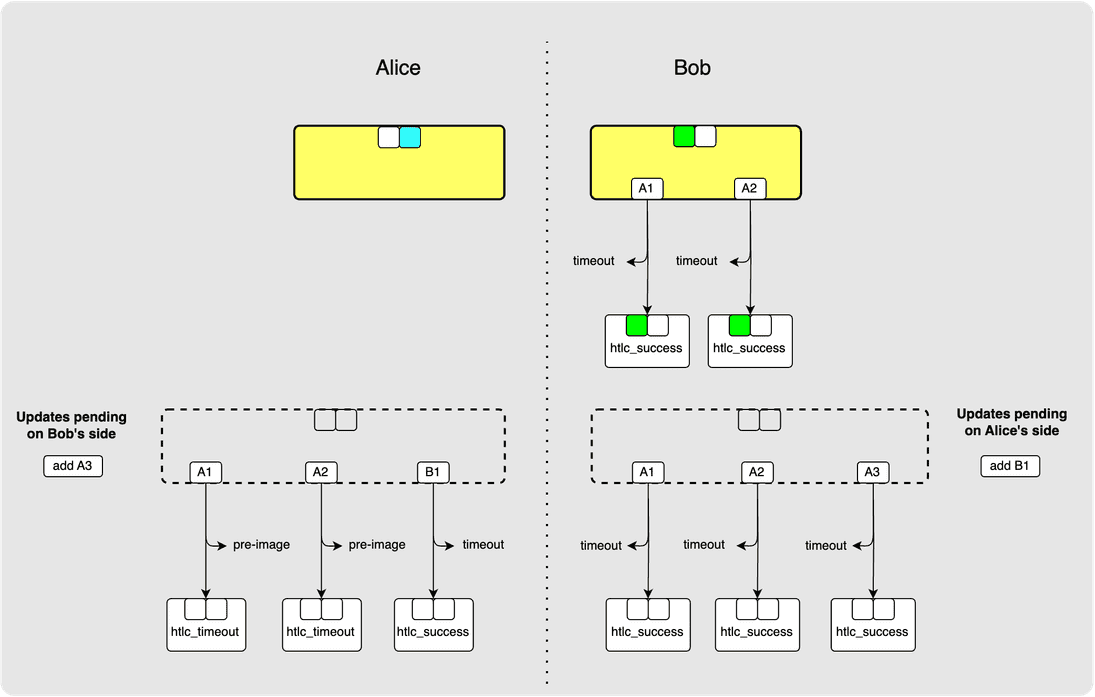
⚙️ Step 7: Bob -> Alice: commitment_signed
Bob wants to irrevocably commit some of the HTLCs so that he can forward them
on, so he finally sends Alice a commitment_signed of his own. This will
include his signature for Alice’s staging-area commitment transaction along with
all the signatures required from him for the second-level HTLC outputs.
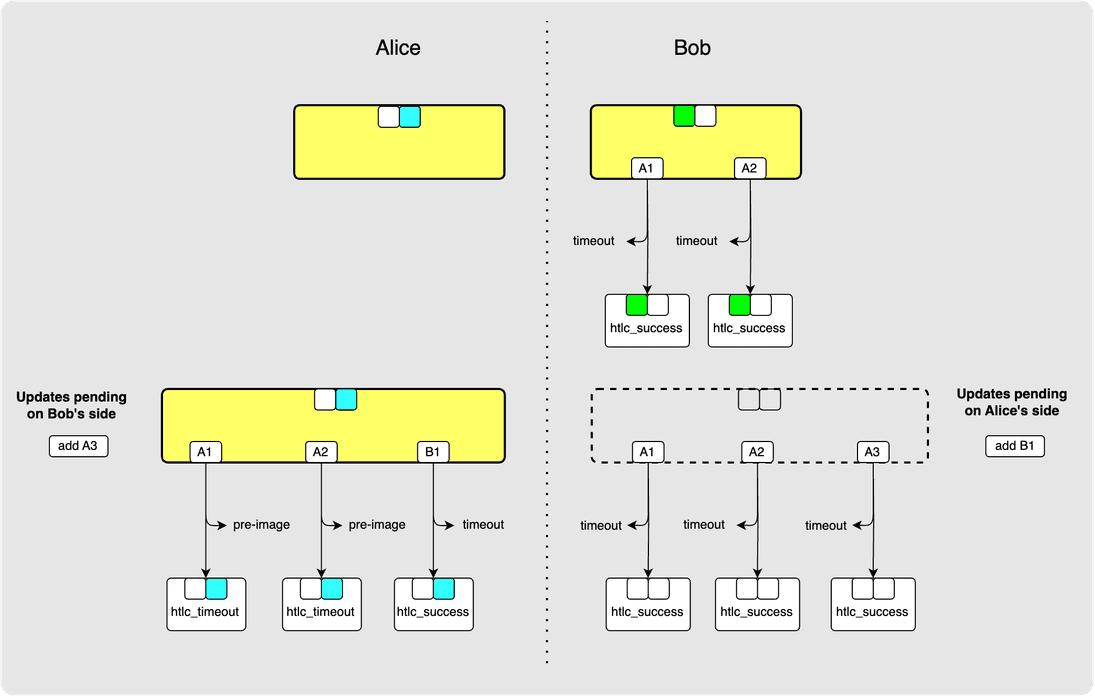
⚙️ Step 8: Alice -> Bob: revoke_and_ack
Just like Bob did previously, Alice responds to the commitment_signed with
a revoke_and_ack in order to revoke her previous state. This also serves as
an acknowledgement to Bob that Alice has received and committed to B1 and so
Bob can now add B1 to his staging area commitment transaction.
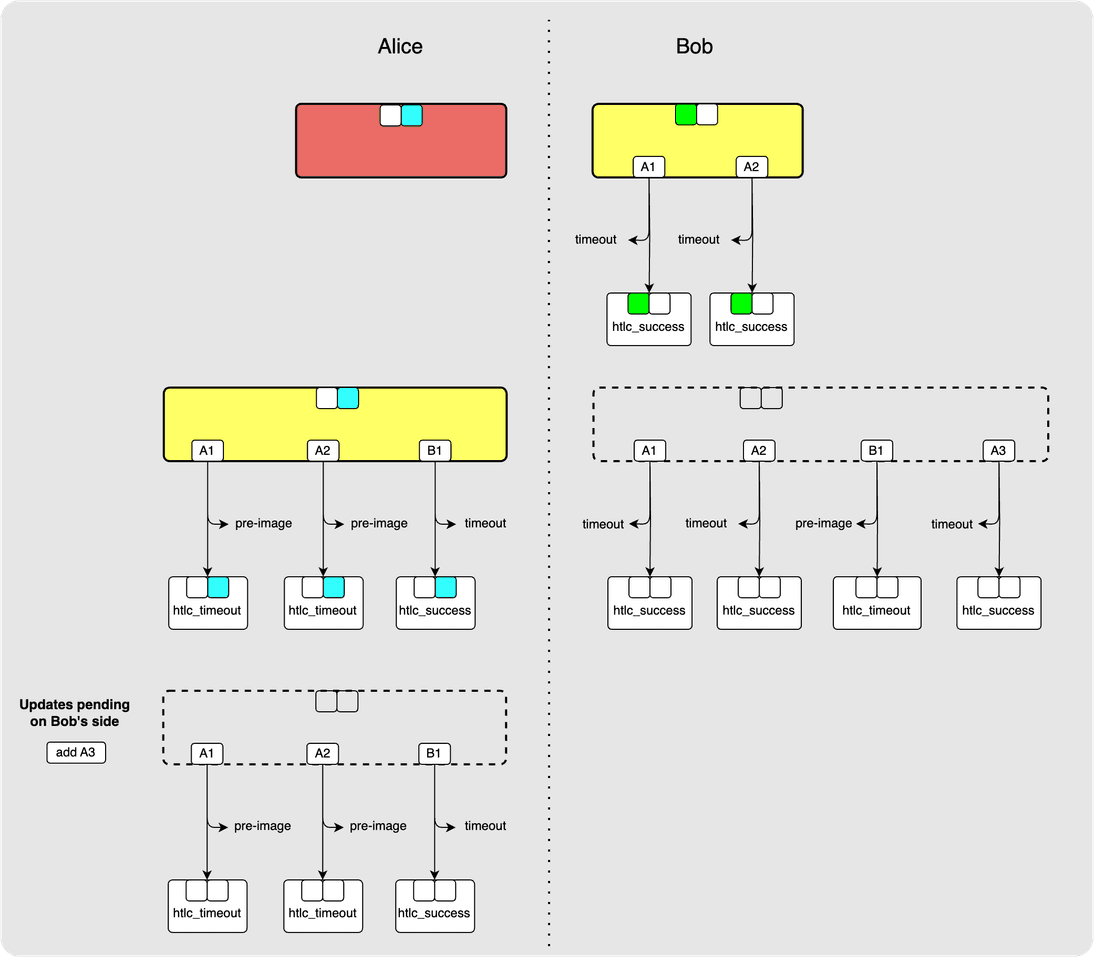
Allow me to clean that up real quick…
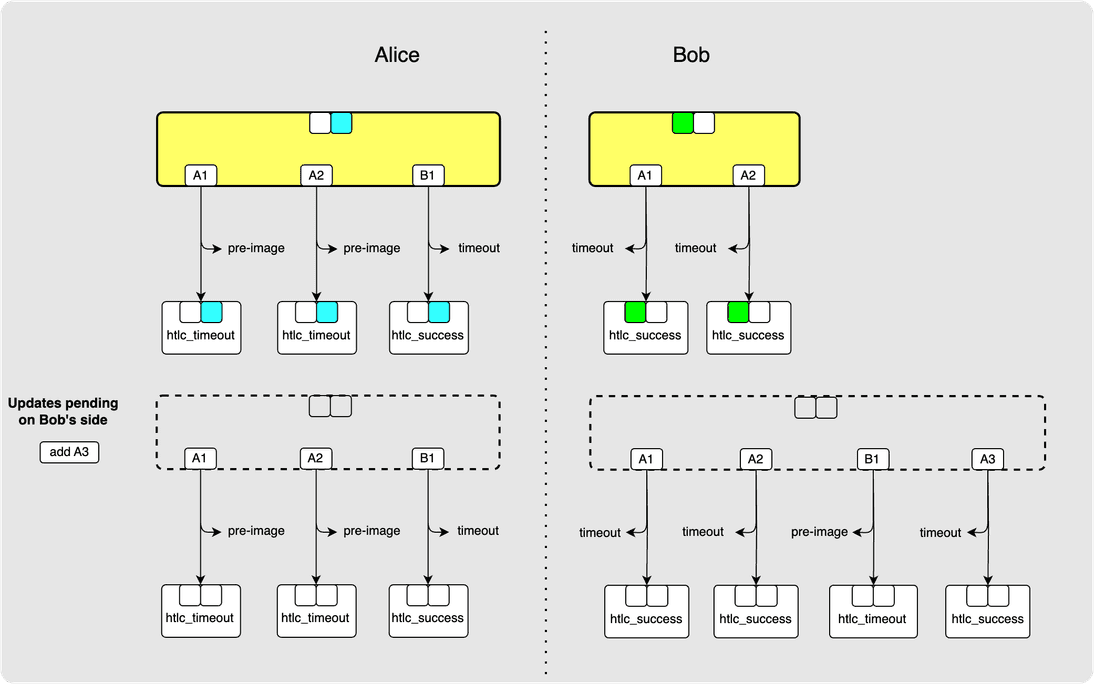
Much better.
At last, we have some irrevocably committed HTLCs! A1 and A2 have
been irrevocably committed. B1 and A3, however, have not since they have not
yet been committed to by both parties.
Let's quickly irrevocably commit B1 and A3.
⚙️ Step 8: Alice -> Bob: commitment_signed
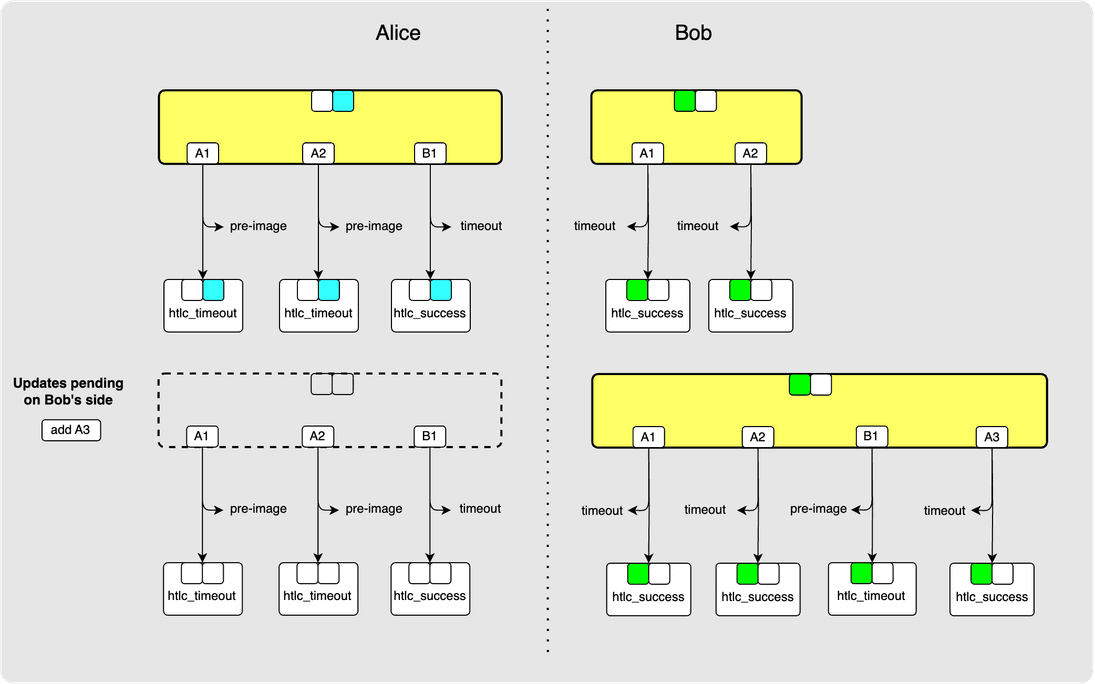
⚙️ Step 9: Bob -> Alice: revoke_and_ack
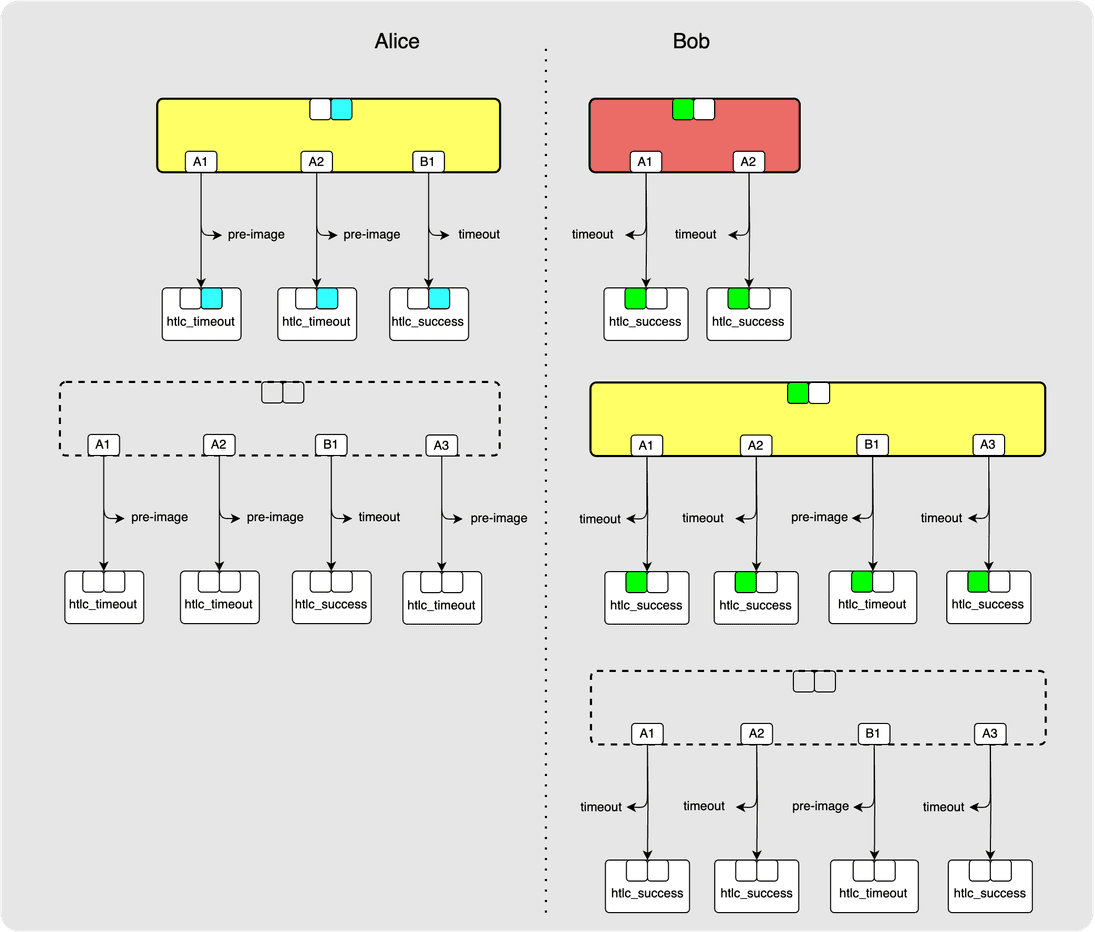
⚙️ Step 10: Bob -> Alice: commitment_signed
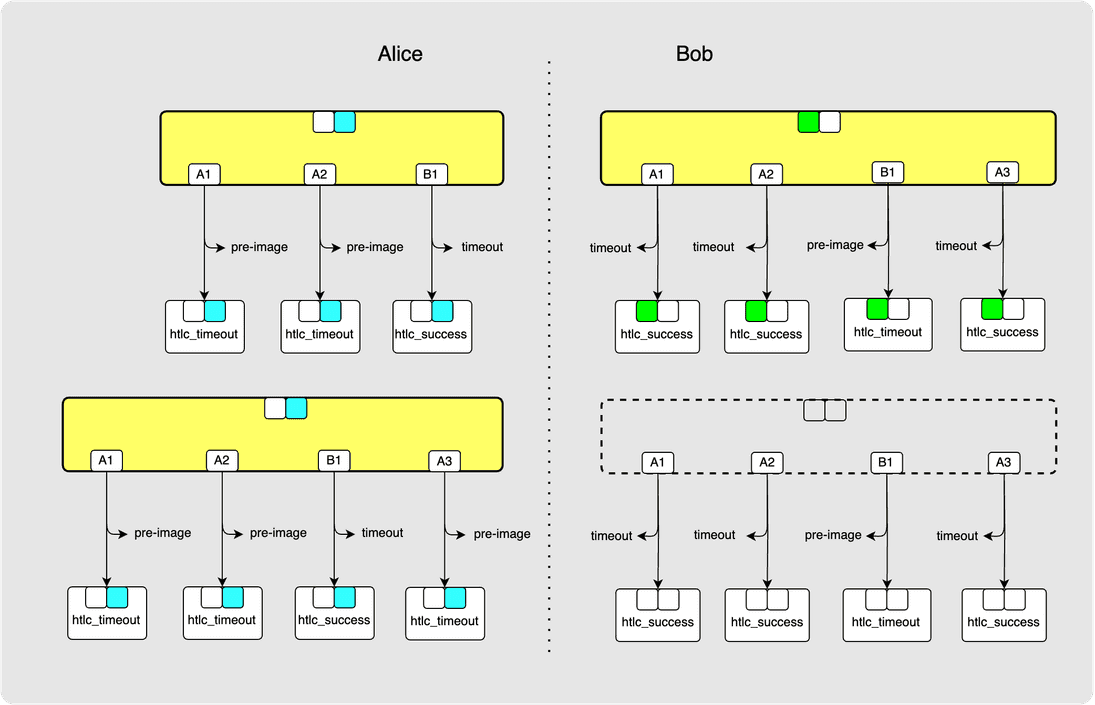
⚙️ Step 11: Alice -> Bob: revoke_and_ack
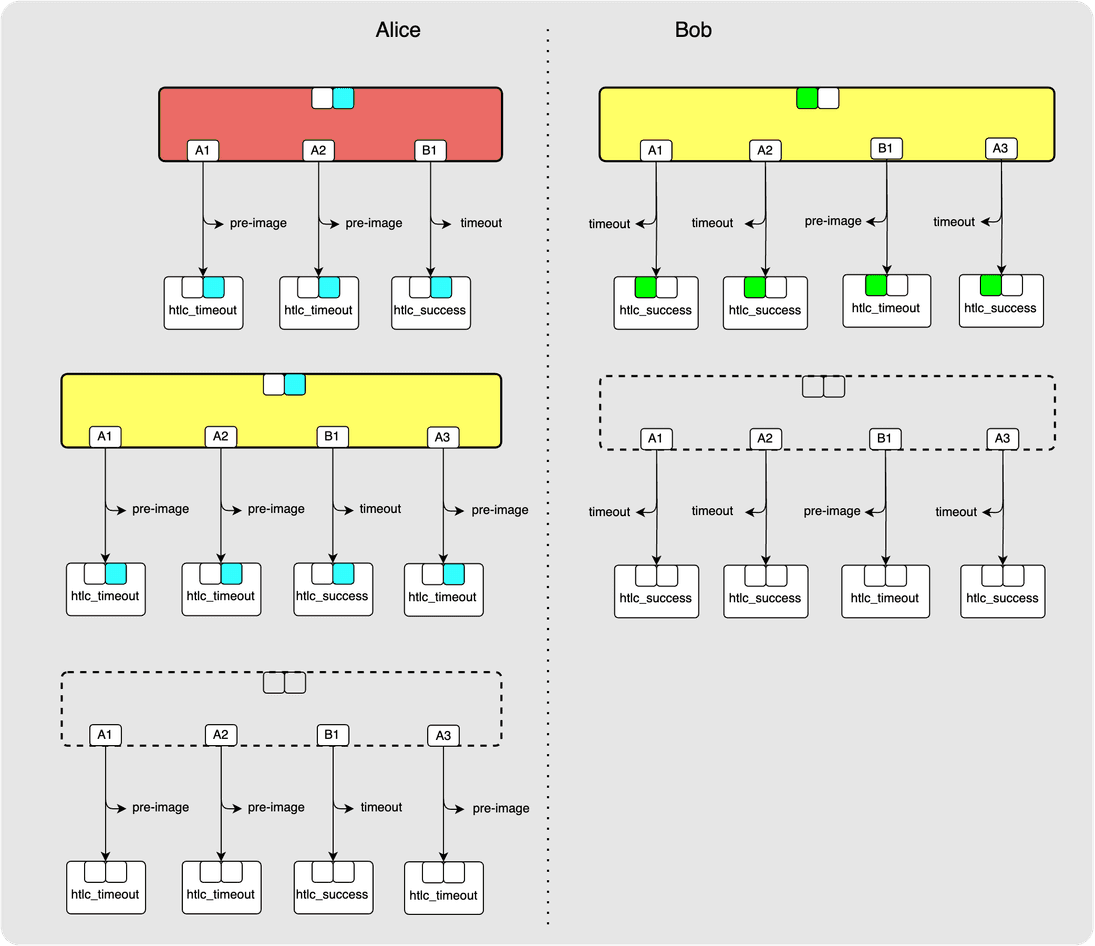
Another clean-up:
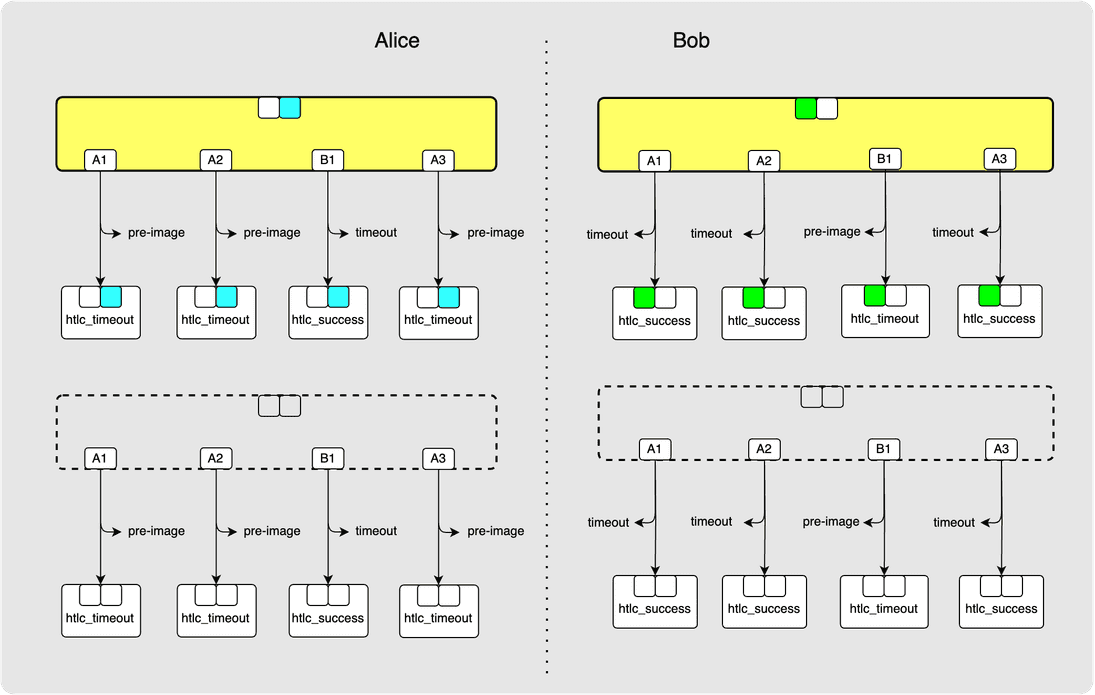
Ok cool! Now all the HTLCs have been irrevocably committed.
Removing HTLCs
You probably get the idea of adding HTLCs now. But how about removing them?
HTLCs are removed if a payment succeeds or if it fails. Note that HTLC removal
messages can only be sent by the peer who did not send the original
update_add_htlc and that HTLC’s are only removable once they have been
irrevocably committed to. Luckily for us, all the HTLCs have been irrevocably
committed, and so we can start removing them now.
⚙️ Step 12: Bob -> Alice: update_fulfill_htlc(A2)
In the best case scenario, an HTLC is removed because it is being fulfilled
meaning that its pre-image is being passed back. This is done with the
update_fulfilled_htlc message which looks as follows:
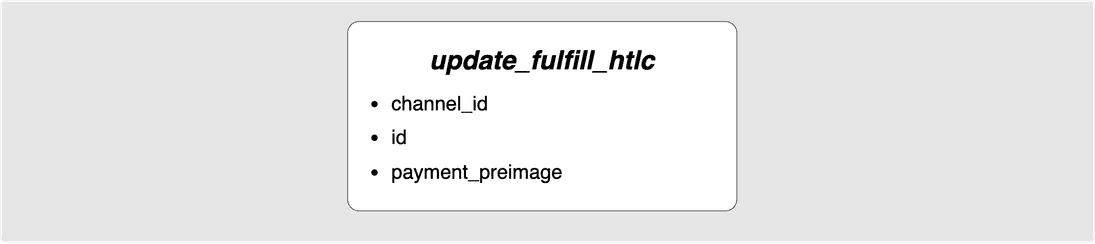
In our example, Bob sends Alice the update_fulfill_htlc message for HTLC A2.
This also demonstrates that the HTLCs don’t need to be removed in the same order
they were added.
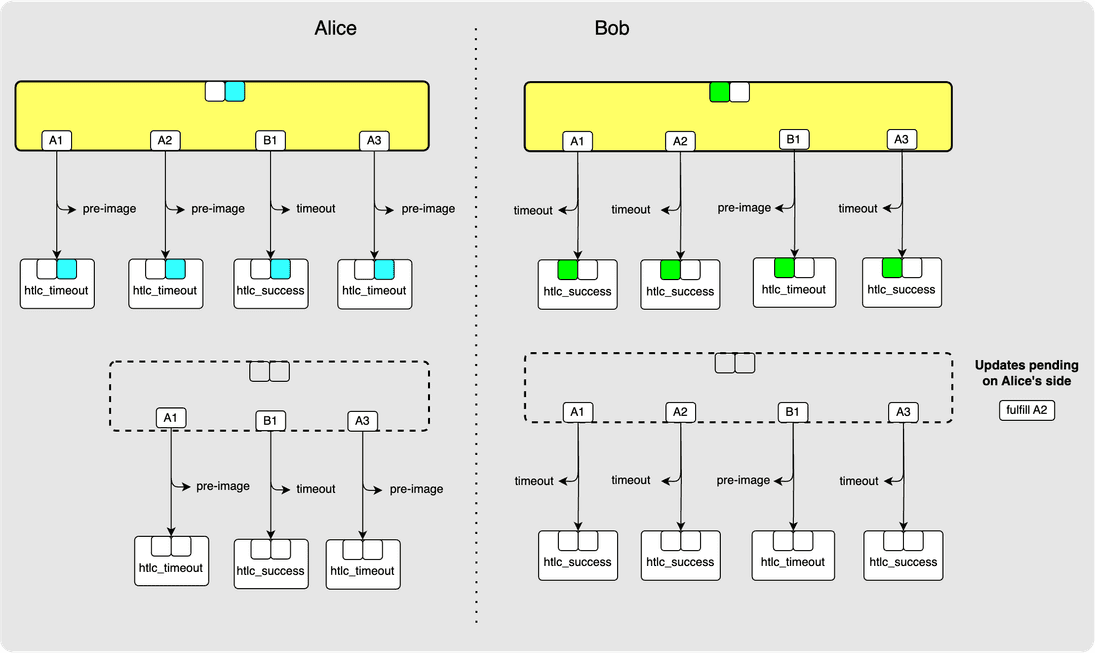
Notice that just like the updates for adding an HTLC, updates for removing an
HTLC will also initially be pending on the receiver side until they have been
acknowledged by a revoke_and_ack. So in our case, Alice removes A2 from her
staging area transaction when she receives the update_fulfill_htlc (and
allocates the HTLC amount to Bob's output) but Bob does not yet remove the HTLC
from his staging area transaction.
Unlike other update messages, there is no need to wait for an HTLC removal to be irrevocably committed if you receive the pre-image for it. You can immediately send the pre-image upstream in order to claim any HTLCs there.
⚙️ Step 13: Bob -> Alice: update_fail_htlc(A1)
HTLCs can also be removed due to payment failures such as HTLCs timing out or if
there was some sort of routing failure such as a specific channel on the path
no longer existing, a hop’s fee requirements not being met, a link not having
sufficient balance etc. Such failures are communicated with the
update_fail_htlc message:
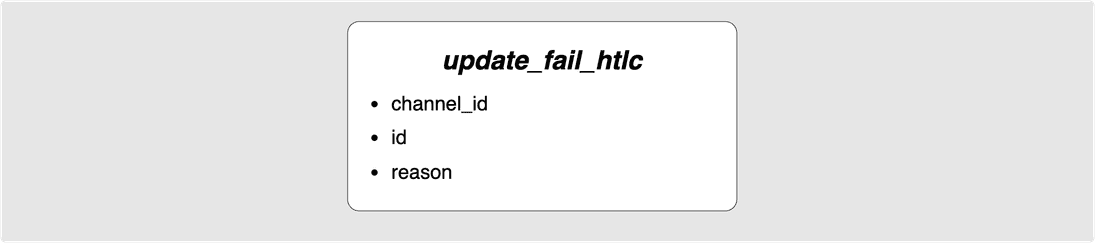
The reason field is an encrypted blob for the sender of the payment in order
to inform them of the failure reason.
After Bob sends Alice the update_fail_htlc message for A1, the state looks
as follows:
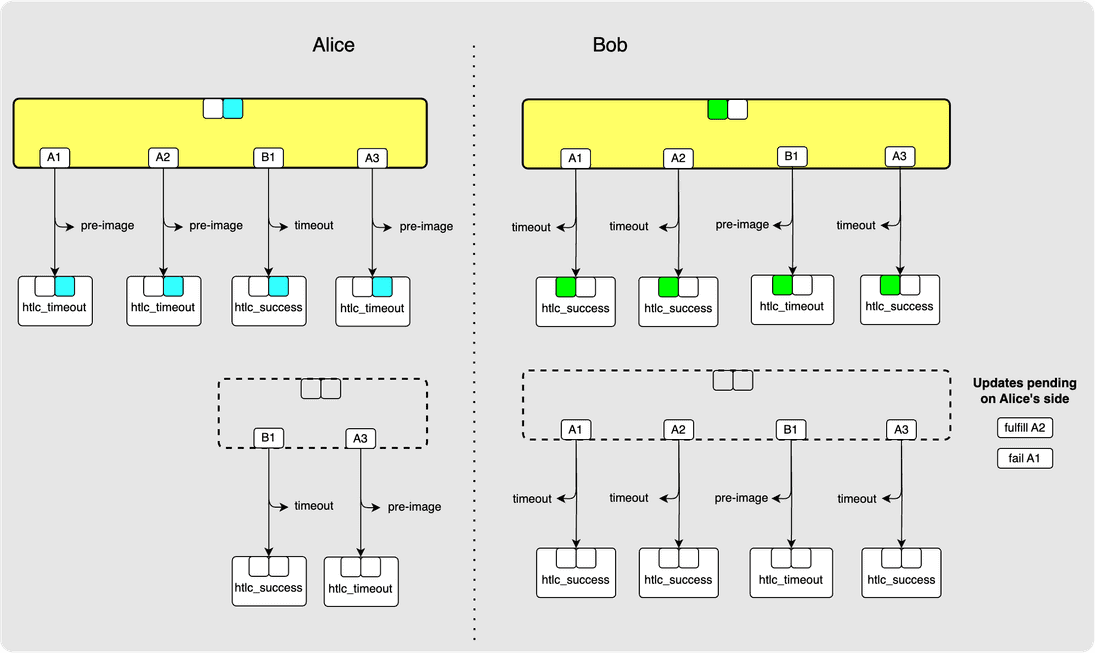
⚙️ Step 14: Bob -> Alice: update_fail_malformed_htlc(A3)
The final message that can be used to remove an HTLC is the
update_fail_malformed_htlc message:
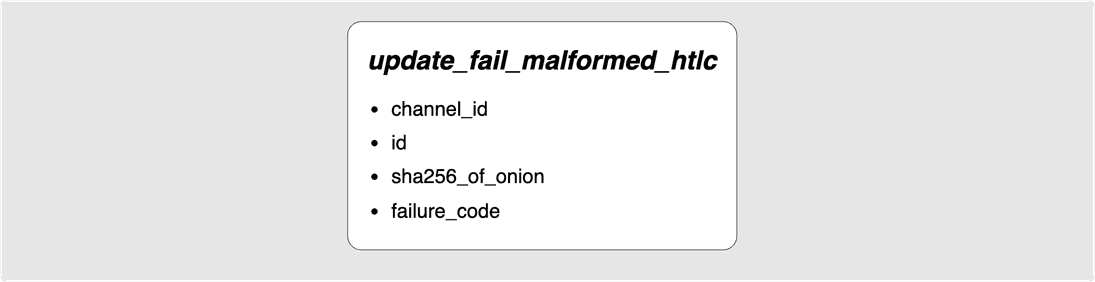
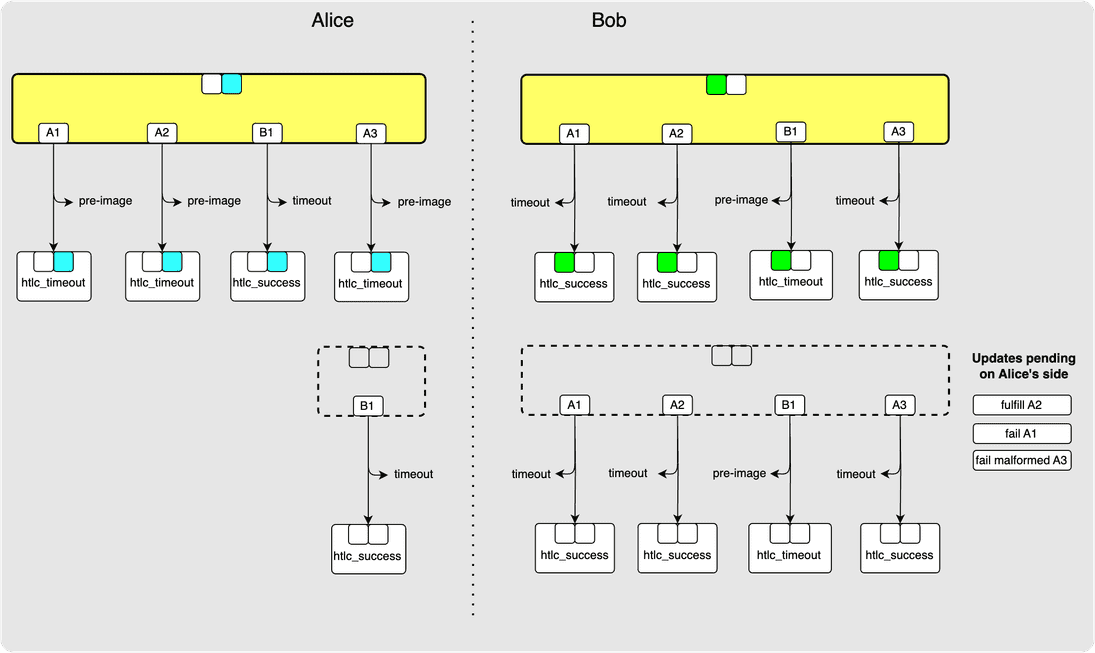
This is sent back if any hop was unable to parse the onion_routing_packet it
received in update_add_htlc. If Bob sends Alice this message for A3, then
the state now looks as follows:
⚙️ Step 15: Alice -> Bob: update_fulfill_htlc(B1)
Alice also initiates the removal of B1 by sending an update_fulfill_htlc
to Bob.
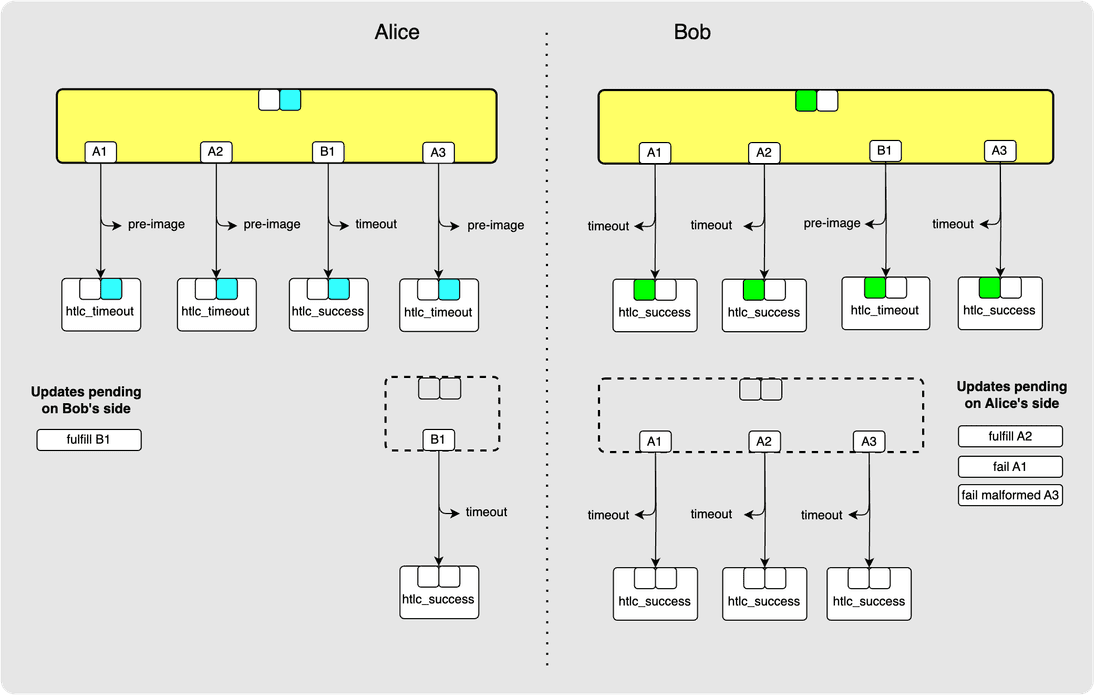
Let’s now clean-up the HTLC removals by irrevocably committing them. This will
require a few commitment_signed-revoke_and_ack flows:
⚙️ Step 16: Bob-> Alice: commitment_signed
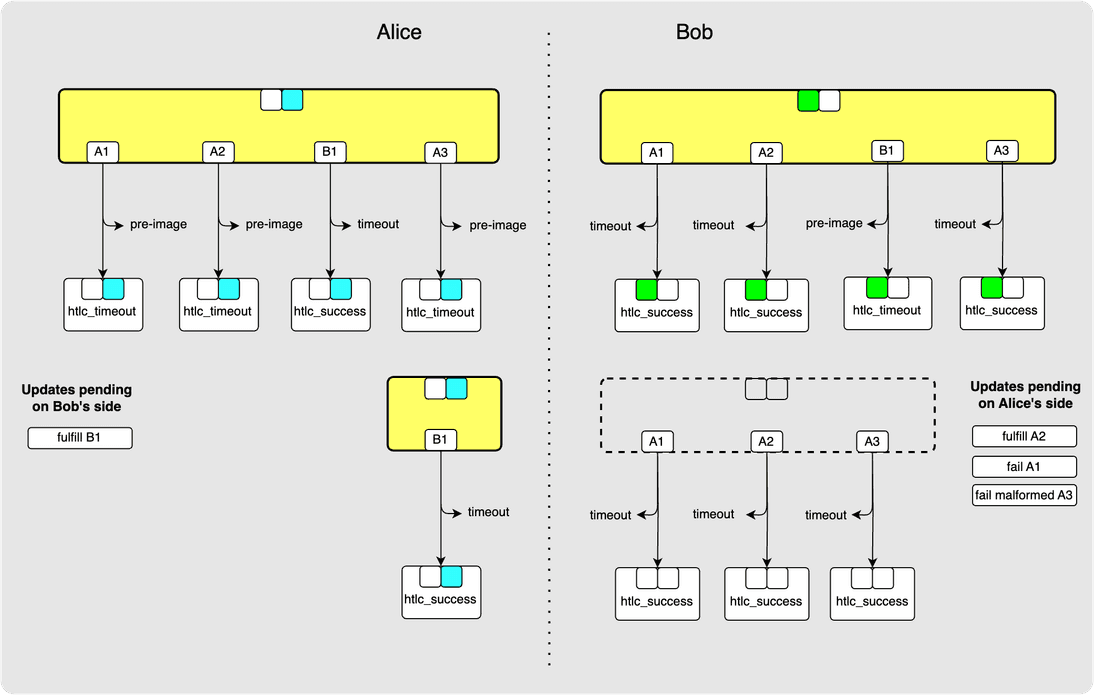
⚙️ Step 17: Alice -> Bob: revoke_and_ack
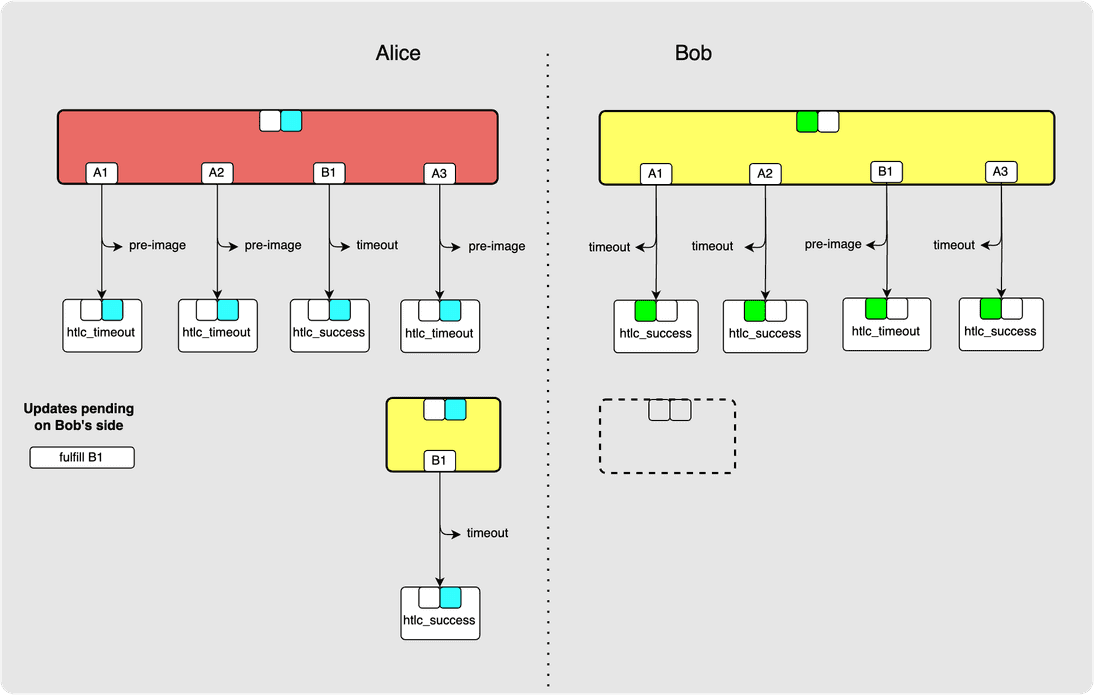
⚙️ Step 18: Alice -> Bob: commitment_signed
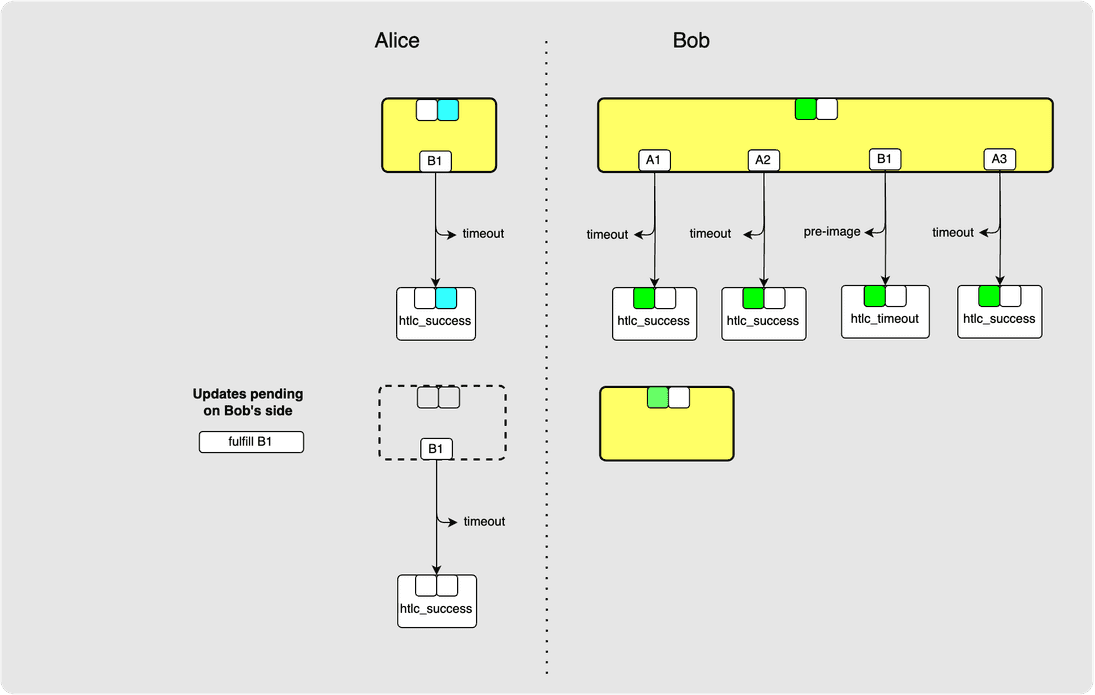
⚙️ Step 19: Bob -> Alice: revoke_and_ack
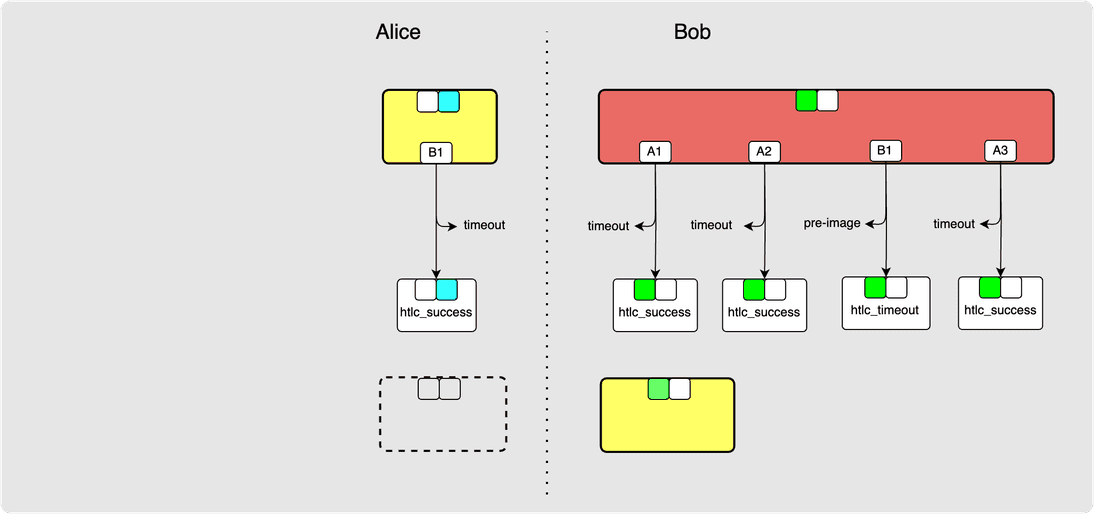
⚙️ Step 20: Bob -> Alice: commitment_signed
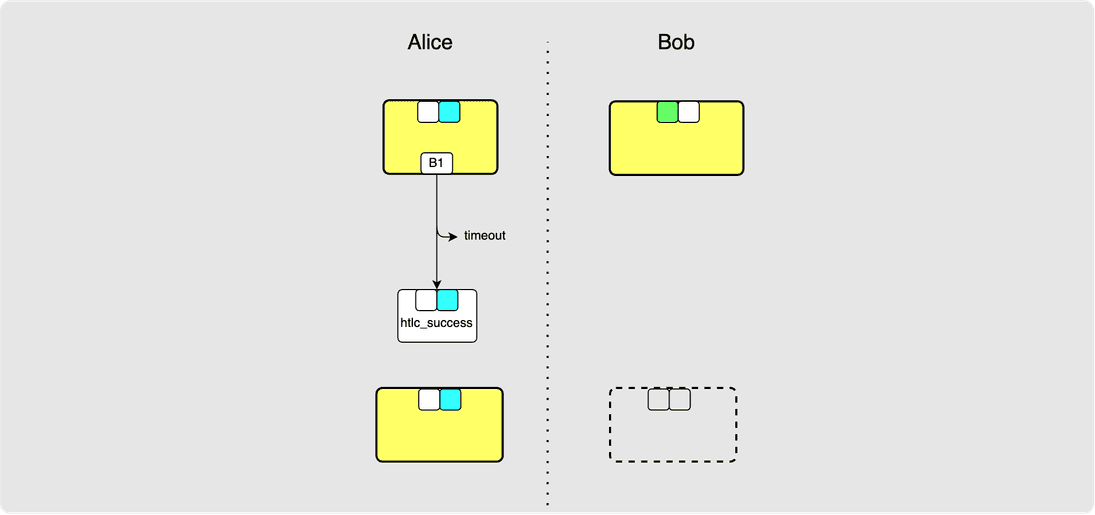
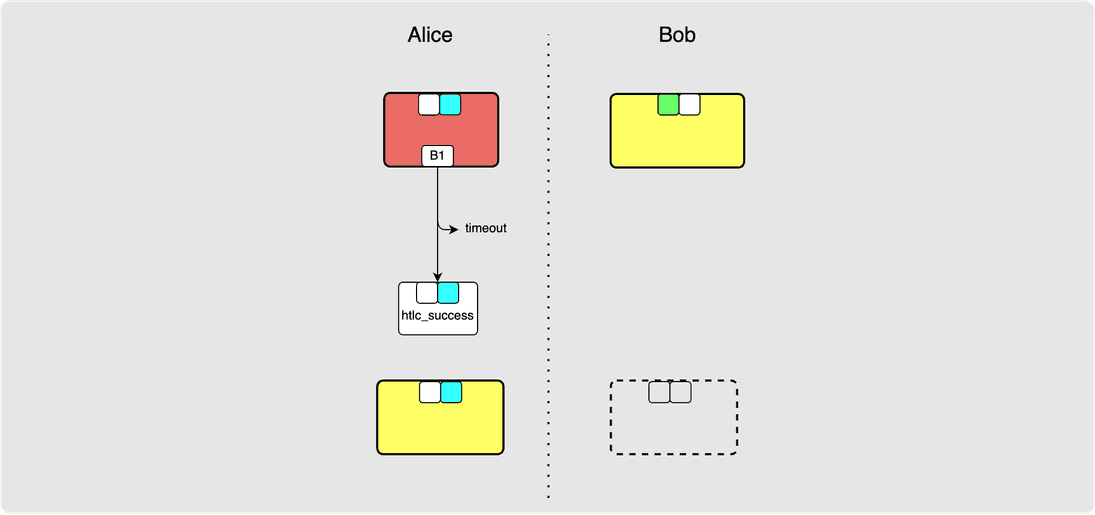
⚙️ Step 21: Alice -> Bob: revoke_and_ack
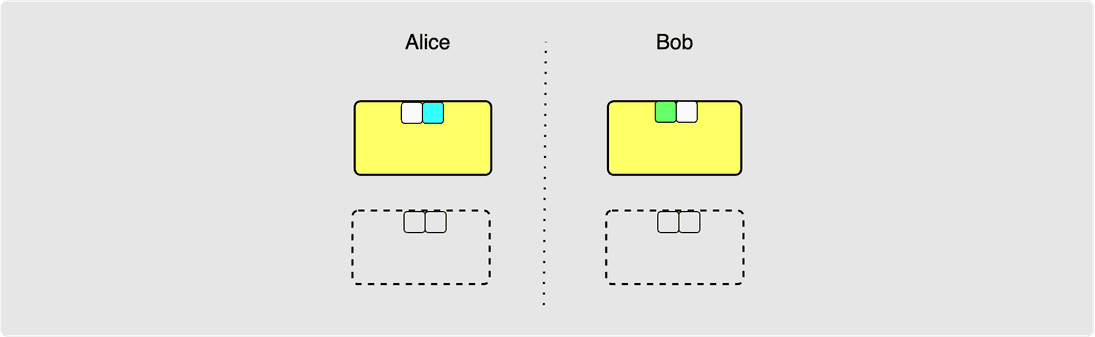
The two valid states now look nice and clean once again:
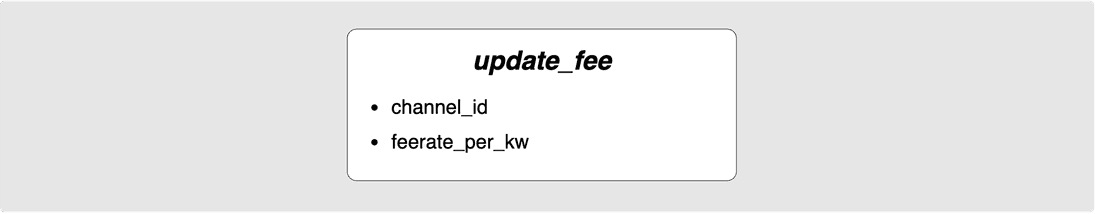
Updating fees
There is one more update_* message that we need to cover and that is
the update_fee message. This message is used to update the fee-rate that the
peers should use when constructing their commitment transactions. The original
fee-rate is decided in the open-channel flow but if the average mempool fee-rate
increases, the channel funder might decide to update the fee of the commitment
transactions so that they have a better chance of getting confirmed in a timely
manner in a force close situation. It could also be that when the channel was
opened, a very high fee-rate was chosen and perhaps a lower fee-rate would be
desired.
This message follows similar rules to other update_* messages in that it must
also be irrevocably committed before it takes effect. The only other extra rule
that applies to this message is that only the channel funder may send this
message.
One thing to note is that with anchor channels, the need to use the update_fee
message is becoming less and less since nodes will be able to use CPFP on the
force-close transaction if required.
Message Retransmission
Something that you may have picked up on while walking through the add/remove
HTLC flow is that explicit acknowledgements for the update_* messages is
delayed until the commitment_signed/revoke_and_ack exchange. That is ok
most of the time since we assume that the underlying transport between the two
nodes (see Bolt 8) is ordered and reliable. However, if the connection
needs to be re-established for some reason, there will be doubt regarding
whether our peer has received the last message that we sent. This is where the
channel_reestablish message comes in. Upon reconnection, before continuing with
the normal operation flow, the peers will exchange this message to make sure
they are on the same page and to determine which messages they possibly need to
re-send to their peer.

Each peer in the channel has their version of the commitment transaction and the
two commitment transactions can be updated independently meaning that the number
of times that one side’s commitment transaction state has been updated (through
the commitment_signed and revoke_and_ack flow) could be completely different
to that of the other side. The next_commitment_number field in the
channel_reestablish message allows us to communicate with our peer the next
commitment_signed that we expect to receive from them. This way, they will
know if we have perhaps missed a commitment_signed from them that they
previously sent before the disconnection. In other words,
next_commitment_number tells the remote peer what we see our latest committed
state to be. Similarly, next_revocation_number is the commitment number of the
next revoke_and_ack that we expect to receive. In other words, this indicates
to our peer which commitment number we think is their latest one. The
your_last_per_commitment_secret is the last per-commitment secret received
from the remote peer which will give the remote peer an idea of the state it has
definitely revoked. my_current_per_commitment_point is the commitment point of
the local party on its last commitment transaction signed by the remote peer (in
other words, the commitment transaction that has not yet been revoked). There
are a lot of checks that a node should do when receiving a channel_reestablish
in order to make sure that all necessary updates are re-sent so that the channel
can continue as normal. There are also some checks that ensure that nodes are
not tricked into revoking a state that should not yet be revoked or tricked into
broadcasting a state that has been revoked. If you are interested in the
details around these checks, see bolt 2.
Note that when a connection re-establish happens, both sides must remove any
un-committed updates from their staging area. If we stick with the git analogy,
they should hit git stash when a reconnection occurs. This means that both
sides will need to re-transmit any update_* messages that were not yet
committed on the other side’s commitment transaction.
Closing a channel cooperatively
Alice and Bob sure had some good times together but all good things must come to an end. Closing a channel in a cooperative way requires the two peers to decide on a final closing transaction that will spend from the funding transaction and will pay each of them their final channel balance immediately.
⚙️ Step 22: Bob -> Alice: shutdown
Bob has decided that it is time to cut ties and sends Alice the shutdown
message.
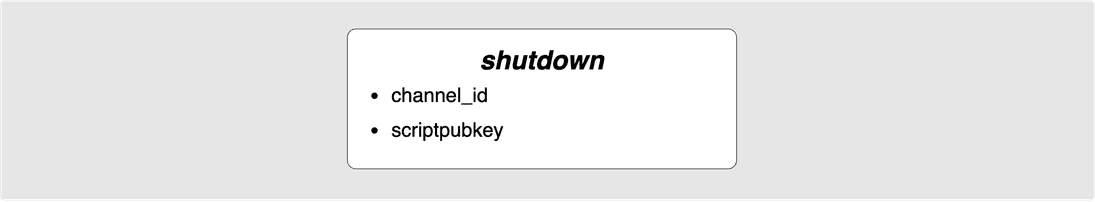
The shutdown message contains the scriptpubkey that Bob would like his final
channel balance to be sent to in the closing transaction. Once Bob has sent this
message, he may no longer send any new update_add_htlc messages. He may only
send HTLC removal and update_fee messages. When Alice receives this message
from Bob, she must respond with her own shutdown message and may also no
longer send any new update_add_htlc messages. Alice and Bob now need to wait
until all remaining HTLCs have been cleared from both commitment transactions.
Since the closing transaction will spend from the funding transaction and
explicitly looks different from the commitment transactions, I’ll re-introduce
some of the details in to the state diagram:

Once all the HTLCs have been cleared, which in our example is already the case, they can start negotiating a fee to use for the final closing transaction. The funder of the channel must start this negotiation. Let’s assume that the funder of this channel was Alice.
⚙️ Step 23: Alice -> Bob: closing_signed
Alice will first choose a fee-rate that she thinks is appropriate for the
closing transaction. She will then use that fee-rate to complete the
construction of the closing transaction and will sign it. She then sends the
closing_signed message to Bob:

The fee_satoshis field tells Bob the fee in satoshis that Alice used to
construct the first closing transaction proposal and the signature contains
Alice’s signature for this proposal. She may optionally also include the
min_fee_satoshis and max_fee_satoshis fields in order to let Bob know that
if he disagrees with her proposed fee_satoshis, then he may send a
counterproposal as long as his counterproposal lies between the provided
minimum and maximum values.
At this point, the channel state looks as follows:
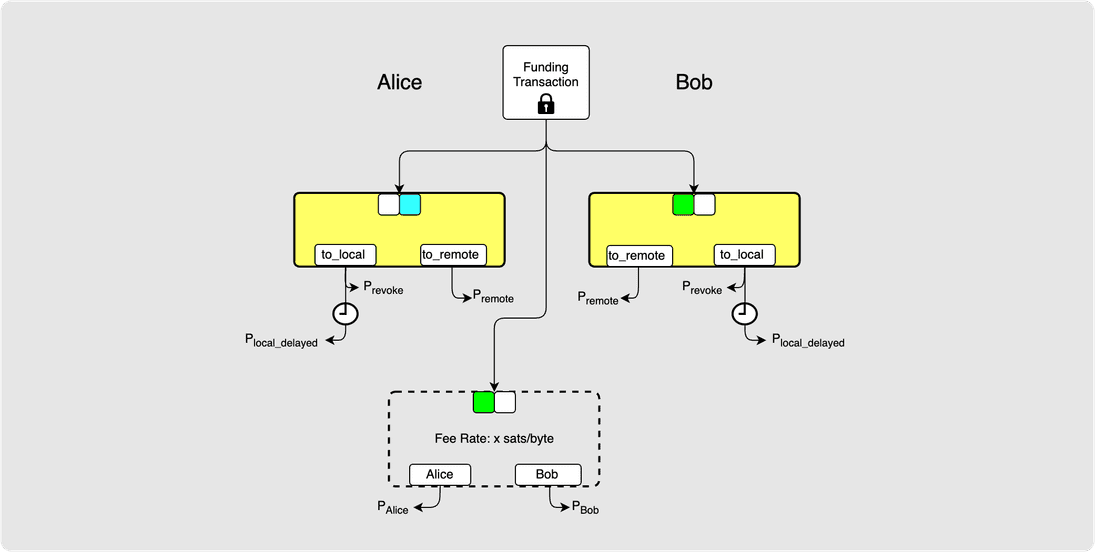
There are two valid commitment transactions that can be signed at any time by
each party to perform a force close, and there is one closing transaction
proposal that uses a fee-rate of x sats-per-byte. This closing transaction
currently only has Alice’s signature and so is not yet valid.
If at this point, Bob is happy with Alice's proposal, he could go ahead and sign the closing transaction using the fee-rate proposed by Alice and could broadcast it and that would be the end of it. But for the sake of the example, let's say that Bob isn't quite happy yet.
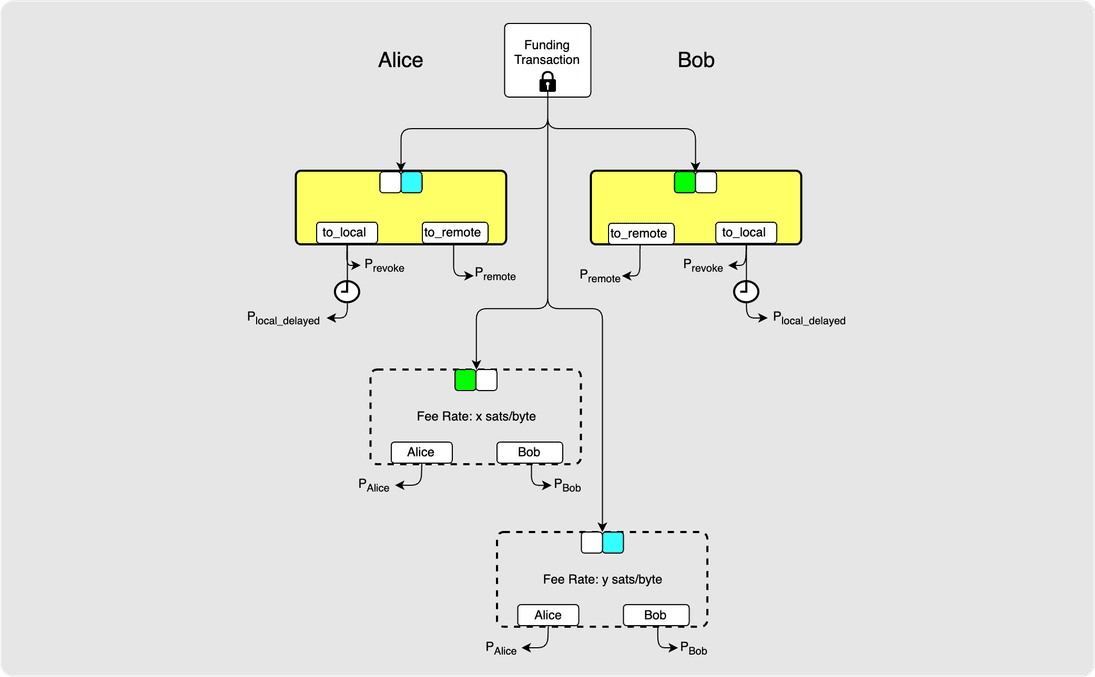
⚙️ Step 24: Bob -> Alice: closing_signed
Bob may decide that the fee rate that Alice used is too low. So he sends a
counterproposal with a new fee rate, y sats-per-byte, along with his
signature for this counterproposal.
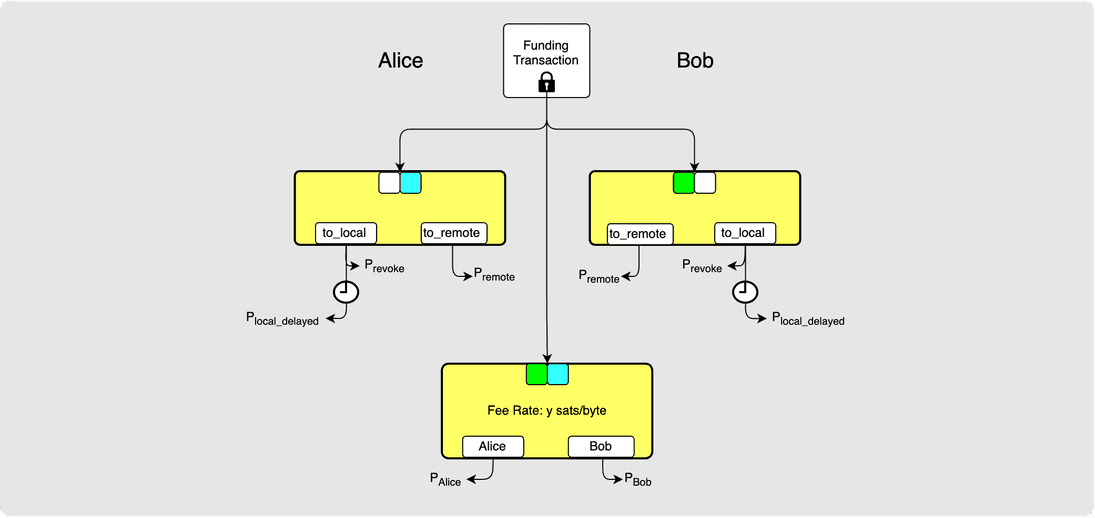
⚙️ Step 25: Alice -> Bob: closing_signed
If Alice is happy with Bob’s counterproposal, then she signs the closing
transaction using the fee-rate suggested by Bob. She may then broadcast the
transaction and call it a day. However, it is recommended in the spec that
Alice send one more closing_signed message to Bob but this time with the
fee_satoshis field set to y sats-per-byte along with her signature for the
transaction. Both parties will now have both signature required in order to
broadcast the final closing transaction that uses the y sats-per-byte fee rate.
Either or both parties may now broadcast the closing transaction to the Bitcoin network. Eventually it will be confirmed, and the channel will officially be closed.
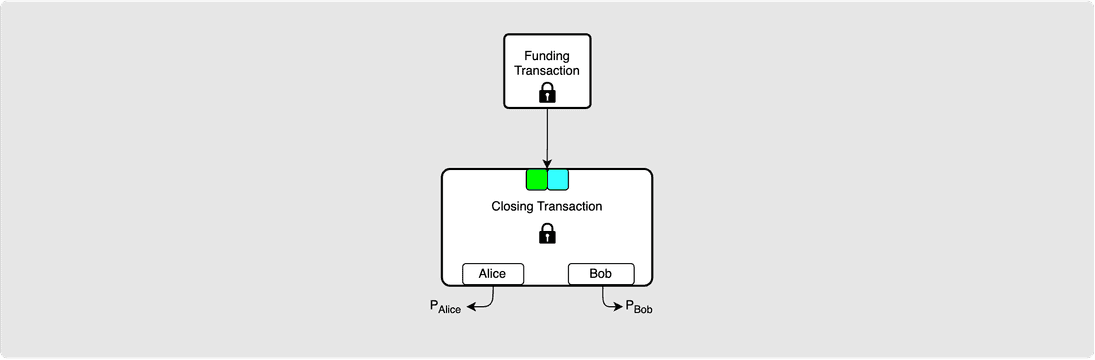
If this channel was a public channel, then any node in the network that had this channel in their routing graph will be able to see that the channel’s funding output has been spent and so will remove the channel from their graph at this point.
The beauty of the channel is that Alice and Bob could have sent millions of HTLCs back and forth throughout the lifetime of the channel and in the end, all that showed up on-chain was the opening and closing transaction.
Alice and Bob lived happily ever after.
Thanks for reading! As always, if anything is unclear or incorrect, feel free to reach out!
Note: this article is a cross-post and you can read the original version on my blog.

